❖ The Movement was formed during the Cold War.
❖ It States that did not formally align themselves with either the United States or the Soviet Union but sought to remain independent or neutral.
❖ It was originated in Asia-Africa Conference held in Bandung, Indonesia in 1955.
NAM’s first conference:
❖ The Belgrade Conference held in 1961.
❖ Under the leadership of India, Yugoslavia, Egypt, Ghana, and Indonesia.
❖ The policy of NAM was based on the 5 principles of Panchsheel.
❖ It has 120 members comprising 53 countries from Africa, 39 from Asia, 26 from Latin America and the Caribbean and 2 from Europe (Belarus, Azerbaijan).

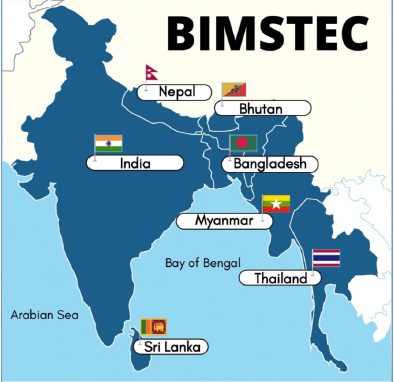
❖ Bay of Bengal initiative for Multi Sectoral Technical and Economic cooperation.
❖ BIMSTEC was established in 1997 as BISTEC with four countries: Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka and Thailand.
❖ In 2004, It was named BIMSTEC, after Myanmar (1997), Nepal (2004) and Bhutan (2004) joined it.
❖ 1st Summit meeting was held in Bangkok in 2004.
❖ Secretariat : Dhaka, Bangladesh.
❖ BIMSTEC has identified 14 priority areas where a member country takes lead.
❖ India is lead country for Transport & Communication, Tourism, Environment & Disaster Management and Counter Terrorism & Transnational Crime.
❖ Established in 1995. It replaced General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs (GATT) which was in place since 1946.
❖ The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement.
❖ India has been a member of GATT since 1948; hence it was party to Uruguay Round and a founding member of WTO.
Functions:
a. Responsible for settling trade disputes between member states
b. Responsible for ensuring the trade policies of member states are in line with the goals of the WTO
c. Member countries are required to inform the WTO about changes in their laws and trade policies.
❖ The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries.
❖ Founded in Baghdad, Iraq, with the signing of an agreement in September 1960 by five countries namely Islamic Republic of Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
Headquarters: Vienna, Austria.
Current OPEC members: Algeria, Angola, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, the Republic of the Congo, Saudi Arabia (the de facto leader), the United Arab Emirates and Venezuela.
❖ Ecuador, Indonesia and Qatar are former members.
❖ An alliance of crude producers, who have been undertaking corrections in supply in the oil markets since 2017.
Members : Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan.
❖ Report : India Energy Outlook
❖ Established in 1974
❖ Main areas of focus: Energy security, Economic development, Environmental awareness and Engagement worldwide.
❖ Headquarters: Paris, France.
❖ Intergovernmental organisation
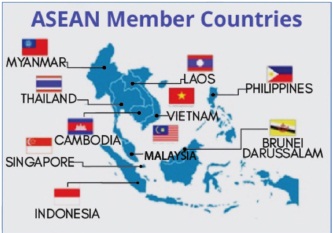
❖ It consists of Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, then Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
❖ Established on 8th August, 1967.
❖ Headquarters: Jakarta, Indonesia
❖ India became a Strategic Partner of ASEAN in 2012.
❖ Established in 1989 on the initiative of the G7.
❖ FATF Secretariat is housed at the OECD headquarters in Paris.
❖ The FATF currently comprises 37 member jurisdictions and 2 regional organisations (European Commission and Gulf Cooperation Council).
Black List Countries:
❖ These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
Grey List Countries:
❖ These countries considered safe haven for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put in the FATF grey list.
❖ World’s centre for cooperation in the nuclear field.
❖ In 1957, It was set up as the world’s “Atoms for Peace” organization.
❖ Headquarters: Vienna, Austria.
❖ The objective of IAEA Safeguards is to deter the spread of nuclear weapons
❖ It is a non-governmental International Organization
❖ It provides a forum for the exchange of knowledge and experience in dam engineering.
❖ Founded in 1928
❖ It is headquartered in Paris, France.
❖ Market development organisation for the gold industry.
❖ Headquarters: UK
❖ It helps to support its members to mine in a responsible way and developed the Conflict Free Gold Standard.
❖ Set up in 1975
❖ Members: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States.
❖ The G20 is an international forum of the governments and central bank governors from 20 major economies.
❖ Formed in 1999.
❖ The first G20 Summit was held in Berlin in December 1999
❖ The G20 Summit is formally known as the “Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy”.
Members: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom and the United States and European Union.
❖ Established with the signing of the SAARC Charter in Dhaka on 8 December 1985.
❖ Secretariat of the Association was set up in Kathmandu on 17 January 1987.
❖ Member States: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
❖ These Nations, at one time known as British Commonwealth, is an organisation of 54 states that were principally below the colonial rule of British Government.
❖ It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalized by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931.
❖ The insignia of this Commonwealth Association is Queen Elizabeth II who is considered the Supreme of the Commonwealth nations.
❖ Formed as the result of an agreement signed by the four countries on November 28, 2009.
❖ Bloc of Brazil, South Africa, India and China.
✦ It is a free trade agreement in the Asia-Pacific region between the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and five of ASEAN's FTA partners Australia, China, Japan, New Zealand, and South Korea.
✦ In November 2012 at the ASEAN Summit in Cambodia, RCEP negotiations were formally launched.
Indian and RCEP:
✦ India, which is also ASEAN's FTA partner, opted out of RCEP in November 2019.
✦ BRICS is the grouping of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
✦ All five are G-20 members.
✦ The First BRIC Summit was held in June 2009 in Yekaterinburg, Russia.
✦ In 2010, South Africa joined the bloc.
✦ During the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014) the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB).
✦ Headquarters: Shanghai
India and BRICS:
✦ India hosted the 4th BRICS summit in 2012 and 8th BRICS summit in 2016.
✦ Established in 1989.
✦ It is a regional economic forum
✦ Headquarters: Singapore
Members: Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, China, Indonesia, Japan; Republic of Korea,Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea; Peru, The Philippines, The Russian Federation, Singapore, Chinese Taipei; Thailand; United States of America; Vietnam.
✦ SCO is a Eurasian economic, political and security organisation
✦ Headquarters: Beijing, China.
✦ It was founded in 2001.
✦ Official languages: Russian and Chinese.
Members:
✦ China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, India and Pakistan
✦ An alliance of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States.
✦ Joint cooperation in signals intelligence.
✦ It began in 1946.
✦ Canada joined the alliance in 1948, followed by Australia and New Zealand in 1956.
✦ It is a group of 27 countries.
✦ In 1957, European Economic Community was established.
✦ In 1993, the EEC changed into the European Union following the new Maastricht Treaty (also known as the Treaty on European Union).
✦ In 2009, Treaty of Lisbon, gave the European Union more broad powers that included being authorized to sign international treaties, increase border patrol, and other security and enforcement provisions.
✦ Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.

✦ Intergovernmental military alliance.
✦ Established by Washington treaty, signed on 4 April 1949.
✦ Headquarters - Brussels, Belgium.
✦ Headquarters of Allied Command Operations - Mons, Belgium.
Importance:
✦ It constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party.
✦ A non-governmental organisation focused on human rights.
✦ It’s objective is to conduct research and generate action to prevent and end grave abuses of human rights, and to demand justice for those whose rights have been violated.”
✦ Headquarters: London
✦ The organisation was awarded the 1977 Nobel Peace Prize for its “campaign against torture.”
✦ A political and economic alliance of six Middle Eastern countries.
✦ Established in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, in May 1981.
Members:
✦ Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman.
✦ Objective: To achieve unity among its members based on their common objectives and their similar political and cultural identities, which are rooted in Arab and Islamic cultures.
✦ Headquarters: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
✦ Established in 1899.
✦ Headquarters : The Hague, Netherlands.
✦ It provides services of arbitral tribunal to resolve disputes that arise out of international agreements between member states, international organizations or private parties.
✦ An intergovernmental organisation
✦ Created in 1982.
✦ Institutionalized in 1984 by the Victoria Agreement in Seychelles.
✦ Headquarters: Mauritius
Members: Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, Réunion (an overseas region of France), and Seychelles.
Observers: China, India, EU, Malta and International Organisation of La Francophonie (OIF).
✦ Formed in 1987
✦ To prevent the proliferation of missile and unmanned aerial vehicle technology capable of carrying greater than 500 kg payload for more than 300 km.
✦ It was formed by the G-7 industrialized countries (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the UK, and the United States).
✦ In 2016, India was inducted into the Missile Technology Control Regime as the 35th member.
✦ The quadrilateral security dialogue
✦ Members: Japan, India, United States and Australia.
Objective: To enhance maritime cooperation between the four nations.
✦ The Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering is a inter-governmental body.
✦ Members are committed to implement international standards against money laundering, the financing of terrorism and financing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
✦ Founded in 1997 in Bangkok, Thailand
✦ Secretariat : Sydney, Australia.
✦ It is an agreement that permits each state-party to conduct shortnotice, unarmed, reconnaissance flights over the others territories to collect data on military forces and activities.
✦ Signed in 1992 and came into effect in 2002.
✦ Currently it has 34 members. Majority of members include North American and European nations like USA, UK, Russia, Turkey.
✦ India is not a member.
✦ Launched in 2000 at Vientiane, Laos.
✦ It seeks for cooperation in tourism, culture, education, as well as transport and communications.
✦ Members: India, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam
✦ Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers
✦ Founded in 1966.
✦ India was a founding member of ADB
✦ It has 67- member countries, including - 48 from the Asian region
✦ Headquarters: Mandaluyong, Philippines.
✦ Established in December 2015
✦ Headquarters: Beijing, China.
✦ It is a multilateral development bank with a mission to improve social and economic outcomes in Asia.
✦ India is a founding member and second largest shareholder in AIIB.
Posted Date: 09/03/2022